Understanding the difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how the body processes glucose (sugar), a key source of energy. The two most common forms are type 1 and type 2 diabetes, and while they share some similarities, they differ significantly in cause, onset, and treatment.
What is the difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes?
For people with type 1 diabetes, the body doesn’t produce any insulin at all. For those with type 2 diabetes the body doesn’t produce enough insulin, or the body can’t use the insulin effectively. Type 2 diabetes is much more common than type 1 diabetes.1
Insulin is crucial for transporting glucose from food out of the bloodstream and into the cells, where it can be used for energy.2
When insulin is able to do this, your blood sugar (glucose) levels stay within a healthy range. In both type 1 and type 2 diabetes the lack of, or inefficiency of, insulin means this doesn’t happen, and the level of glucose in the blood becomes too high.2
Treatment is needed to bring blood sugar levels down so that the body can function properly. Lack of treatment in the long term can result in complications.
What is type 1 diabetes?1
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks itself, destroying the beta cells in the pancreas that produce insulin. You can’t prevent type 1 diabetes, and right now, there is no cure.
Type 1 diabetes makes up about 5-10% of all diabetes cases. Previously type 1 diabetes was called juvenile diabetes, since it often starts in childhood, but you can develop type 1 diabetes at any age. Sometimes it’s hard to tell the difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes at diagnosis because they can have similar symptoms. In fact, misdiagnosis of type 2 diabetes occurs in about 40% of adults with new type 1 diabetes. Over time, the correct diagnosis usually becomes clear.
What is type 2 diabetes?1
Type 2 diabetes is the most common type of diabetes, accounting for 90-95% of all cases. In type 2 diabetes either the body doesn’t produce enough insulin, or the body can’t use the insulin properly - this is called insulin resistance. Insulin resistance means the body has a decreased biological response to insulin. Unlike type 1 diabetes, the symptoms of type 2 often develop slowly and can be hard to notice at first. Many people don’t realize they have it until it’s found during a routine check-up.
Symptoms of type 1 diabetes3
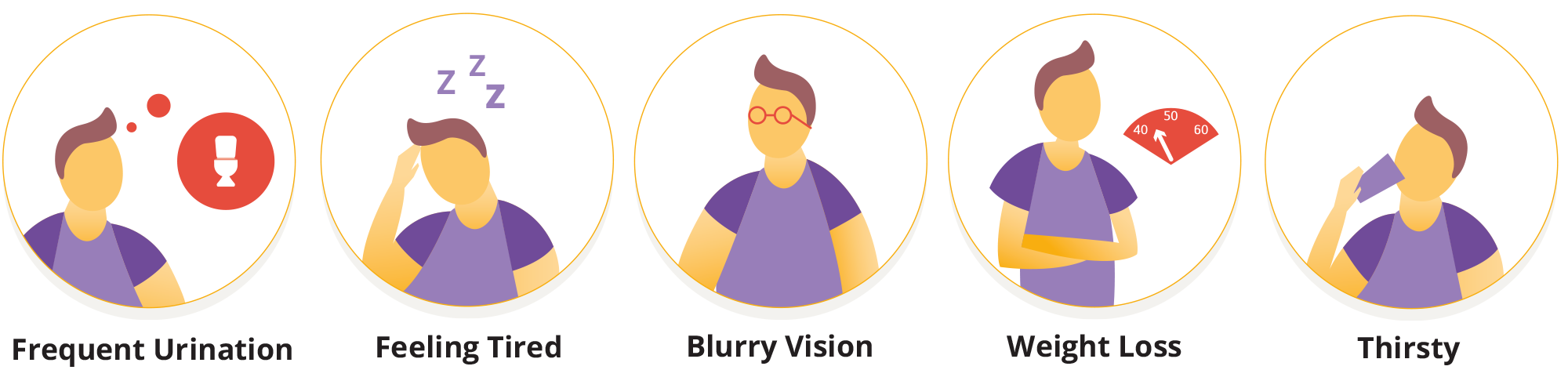
The symptoms of type 1 diabetes can develop very quickly. It is advised to seek medical advice if you start to display the following symptoms:
- increased thirst and urination
- feeling very tired
- losing weight without trying
- increased hunger
- blurred vision
- fruity-smelling breath

Treatment for type 1 diabetes
Because people with type 1 diabetes don’t produce any insulin, they need to take insulin to treat the condition. This is done through daily injections by syringes or insulin pens. Frequently checking blood sugar levels via fingerstick testing, or a continuous glucose monitor (CGM/sensor), is also an important part of type 1 diabetes management.
It helps to determine how much insulin is needed to keep blood glucose within a safe and healthy range.
This can help to prevent glucose levels from running too high (also known as hyperglycemia) or too low (also known as hypoglycemia) for sustained periods of time.
Treatment for type 2 diabetes4
Some people manage their type 2 diabetes through diet and exercise, but many people require medication to help keep their glucose levels in range.
These are the main treatments for type 2 diabetes:
- Eating well and moving more
- Weight loss
- Medications, including insulin
- Insulin pumps
- Automated Insulin Delivery (AID) Systems
Who could consider using an insulin pump as part of their diabetes care?
Are insulin pumps used for type 2 diabetes in the US?
Can Omnipod be used for type 2 diabetes in the US?
Looking for more? Explore articles on how blood sugar levels work, explanations of hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) and hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), their causes, symptoms, and how to manage them effectively.
Other forms of diabetes1
Type 1 and type 2 diabetes are the most common, but there are many other, rarer types of diabetes.
Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy. Many cases of GDM represent preexisting hyperglycemia that is detected by routine screening in pregnancy.
Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults (LADA) sits between type 1 and type 2 and is sometimes called type 1.5 diabetes.
People with LADA can be misdiagnosed as type 2, as the destruction of the beta cells occurs much slower than with type 1 diabetes.
This means that some people may manage their symptoms with diet, exercise and oral medications at first, but will ultimately need to treat LADA with insulin.
Maturity onset diabetes of the young (MODY) is a rare form of diabetes that occurs due to a single gene mutation, with onset at an early age, classically before age 25 years.
What should I do if I’m worried I might have diabetes?4
Type 1 diabetes symptoms can develop very quickly, while the symptoms of type 2 diabetes are often less obvious and can go unnoticed.
Book an appointment with your healthcare provider if you are experiencing the following:
- feeling very thirsty
- peeing more frequently than usual, particularly at night
- feeling very tired
- weight loss and loss of muscle
- blurred vision
Frequently Asked questions
What is Type 1 Diabetes?
What is Type 2 Diabetes?
What tests are used to diagnose type 1 vs type 2 diabetes?
How do doctors diagnose type 1 vs type 2 diabetes?
Continue reading:
Related Articles
References and Disclaimers
1- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee; 2. Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2025. Diabetes Care 1 January 2025; 48 (Supplement_1): S27–S49. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc25-S002
2- Insulin - International Diabetes Federation - https://idf.org/about-diabetes/diabetes-management/insulin/
3 - Type 1 Diabetes - NIDDK - https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/overview/what-is-diabetes/type-1-diabetes
4 - Type 2 Diabetes - NIDDK - https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/overview/what-is-diabetes/type-2-diabetes
This information is not a replacement for medical advice or training. Please always speak to a qualified healthcare professional about your options.
The information and other content provided in this article, or in any linked materials, are not intended and should not be construed as medical advice, nor is the information a substitute for professional medical expertise or treatment. If you or any other person has a medical question or concern, you should consult with your healthcare provider. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something that have read on this blog or in any linked materials. If you think you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. The opinions and views expressed on this blog and website have no relation to those of any academic, hospital, health practice or other institution.
The Omnipod® 5 Automated Insulin Delivery System is indicated for use by individuals with type 1 diabetes mellitus in persons 2 years of age and older and type 2 diabetes mellitus in persons 18 years of age and older. The Omnipod 5 System is intended for single patient, home use and requires a prescription. The Omnipod 5 System is compatible with the following U-100 insulins: NovoLog®, Humalog®, and Admelog®.
Available products subject to current insurance coverage and product indication for use. Insulet can only support onboarding for those customers within the product indication.
Refer to the Omnipod 5 Automated Insulin Delivery System User Guide and www.omnipod.com/safety for complete safety information including indications, contraindications, warnings, cautions, and instructions. Warning: DO NOT start to use the Omnipod 5 System or change settings without adequate training and guidance from a healthcare provider. Initiating and adjusting settings incorrectly can result in over-delivery or under-delivery of insulin, which could lead to hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia.