Insulin Pumps, Explained
Are you thinking about using an insulin pump to manage your diabetes?
There’s a lot to consider, and terms like ‘patch pump’ and ‘closed-loop’ might be new to you. Let’s find out what an insulin pump is, and how insulin pump therapy works.
What is an insulin pump?
An insulin pump is a small, wearable device that delivers insulin continuously throughout the day and night, in very small doses. Insulin pump technology attempts to more closely mimic physiologic insulin delivery, to help achieve improved blood glucose values.1
Insulin pumps are an alternative way to deliver insulin for people with diabetes, in place of multiple daily injections (MDI).
Insulin pump usage has increased dramatically in the United States from less than 7,000 users in 1990 to over 350,000 users in 2019.1
Having different insulin delivery options means you can choose what suits your health and lifestyle best. Your healthcare provider should help you decide, based on your needs, what would work best for you.
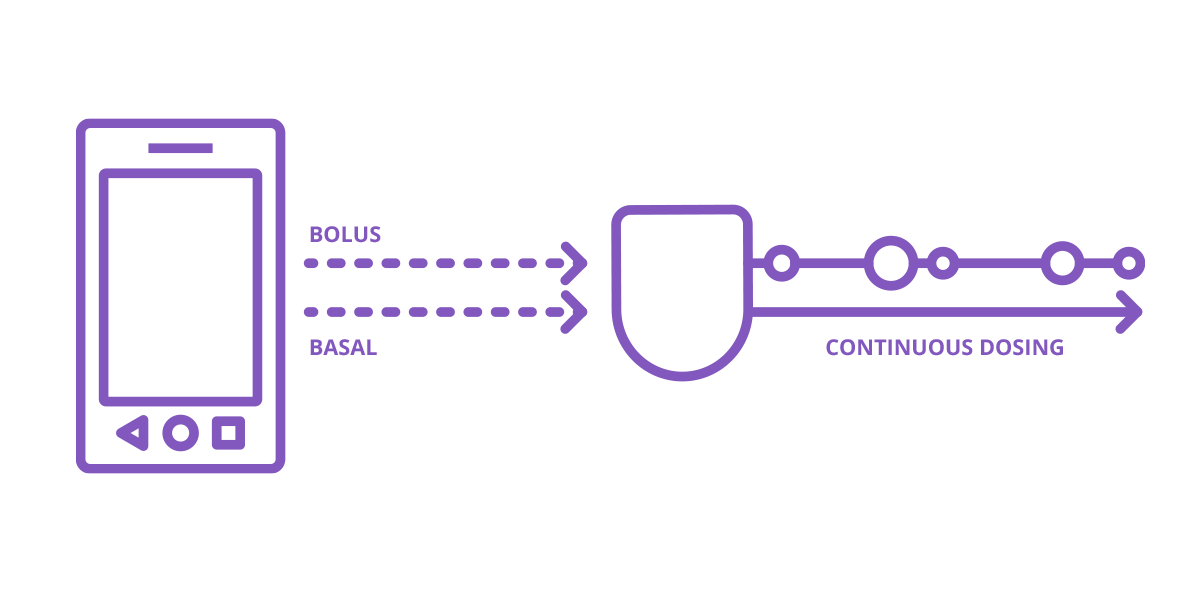
A continuous amount of insulin is delivered 24 hours a day through a cannula, a small flexible tube, placed under the skin. This is known as basal, or background insulin.
Additional insulin can be delivered for meals and high blood glucose values (corrections) - these are known as bolus doses.2
Tubed pumps and tubeless pumps
Pumps can come with tubing and come without tubing. What’s the difference? Will one fit your lifestyle?
Tubed pumps
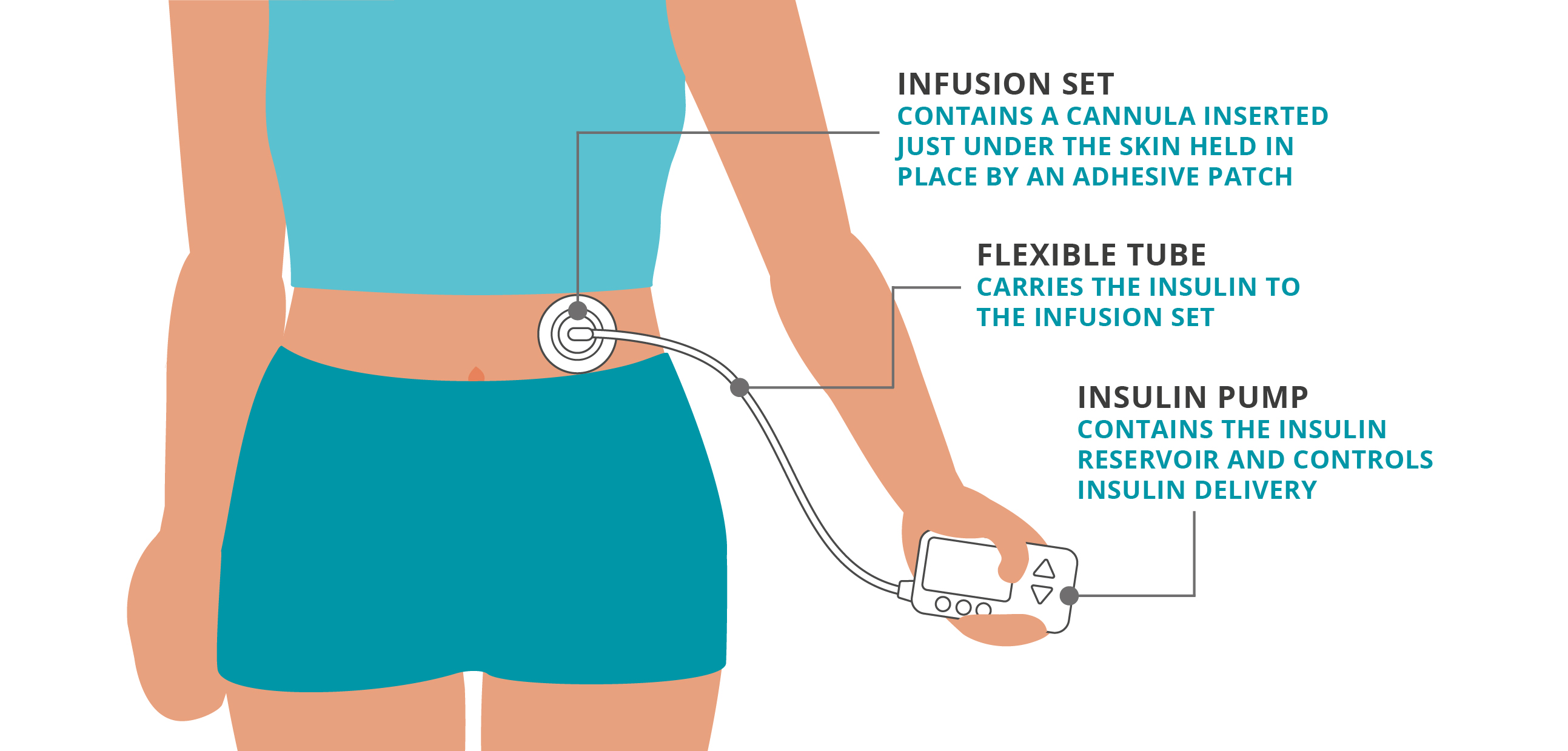
A traditional tubed pump contains the insulin in the pump itself, in the reservoir. The insulin flows from the pump through a length of tubing, and then into the body via a cannula adhered to the skin. In some cases, the pump is worn directly on the body however in most cases the pump is worn on your clothing such as on your belt or in your pocket.
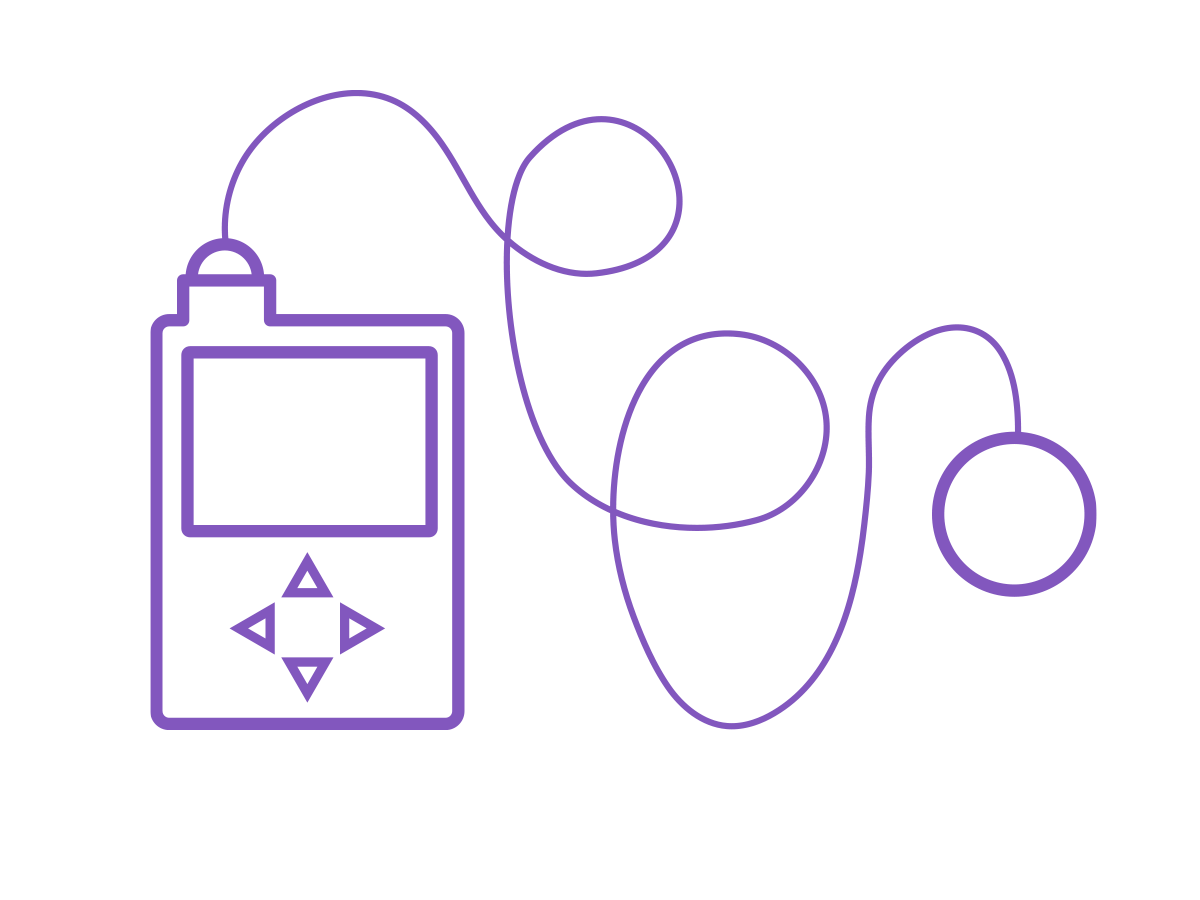


Traditional tubed pumps use the following parts to deliver continuous insulin.
Infusion set: contains a cannula inserted just under the skin held in place by an adhesive patch
Flexible tube: carries the insulin to the infusion set
Insulin pump: contains the insulin reservoir and controls insulin delivery

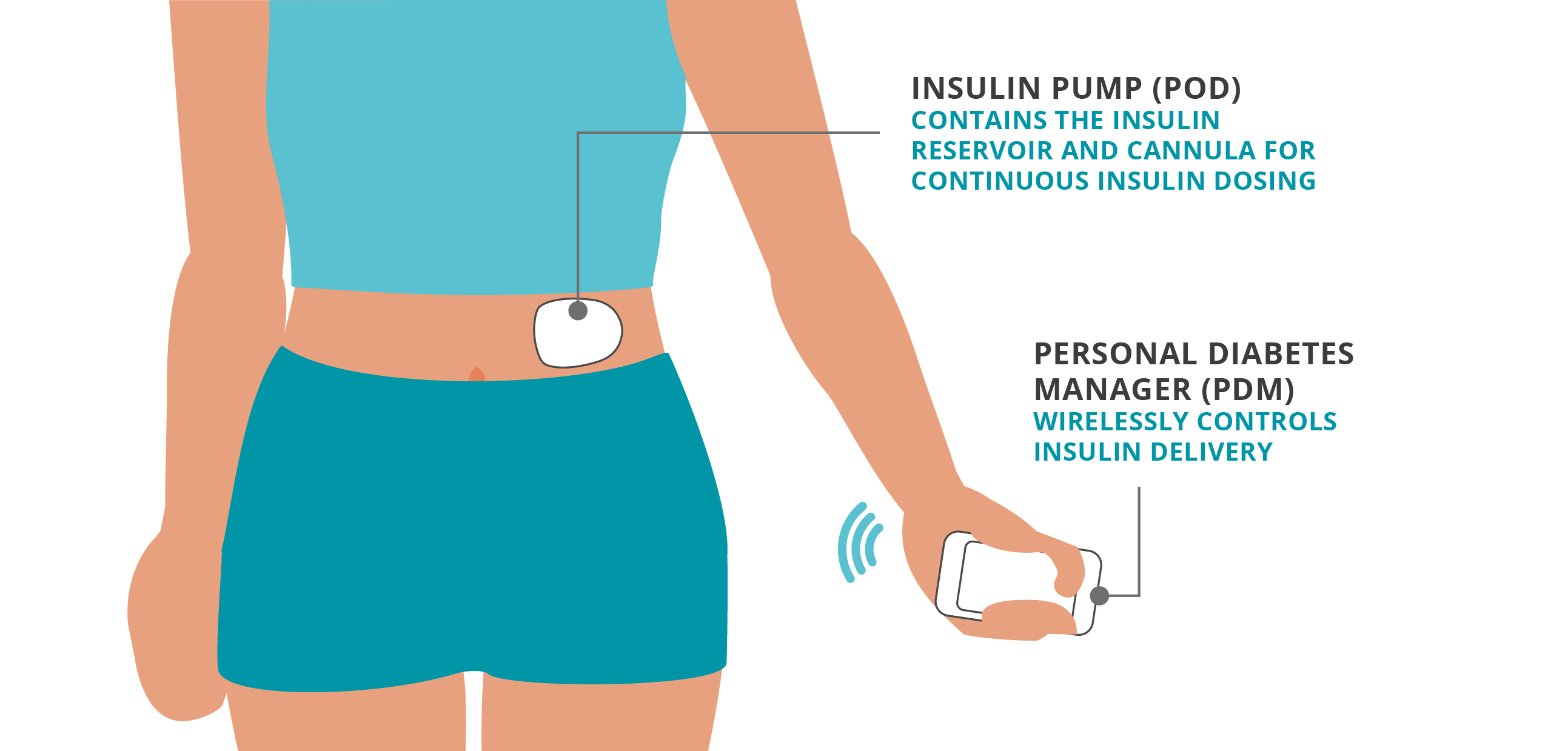
Tubeless pumps
For those who do not want tubing connecting the pump to an infusion set there are what is referred to as Tubeless pumps.
This category of pump is often called a “patch” pump. A patch pump is a small insulin pump that attaches to the skin and delivers insulin via a small, flexible tube that resides directly under the device (cannula). This device is often called a “tubeless” insulin pump since the patch does not have a longer tube connecting it to an insertion set.
The user fills the patch pump with insulin. The insulin is delivered just under the skin through a cannula. Patch pumps are typically controlled by a provided remote controller or compatible smartphone.
Insulin pump (Pod): contains the insulin reservoir and automated cannula for continuous insulin dosing
Personal Diabetes Manager (PDM)/Controller: device that wirelessly controls insulin delivery

Pod Therapy with Omnipod®
One brand of patch pump is Omnipod®, used in Omnipod DASH and Omnipod 5 Systems. The Omnipod pump itself, called a “Pod”, is filled with rapid acting insulin and applied to the body providing up to 72 hours or three days of insulin as an alternative to multiple daily injections. Each Pod is disposable and thrown away every three days or when the insulin is depleted. The user then applies and starts a new Pod. The Pod can be manually controlled via the free PDM (Omnipod DASH) or the free Controller or compatible smartphone with Omnipod 5 (omnipod.com/compatibility). The latest model, the Omnipod 5 is an AID system or Automated Insulin Delivery System and requires a compatible sensor as part of the system.
Insulin Pumps and CGM sensors
Non-Automated Insulin Delivery Systems
People can wear both an insulin pump and a CGM sensor, as they are separate devices. But wearing both devices does not mean that they will interact and does not mean the insulin pump will automatically adjust insulin based on CGM values.
In these situations where they do not interact, a patient can wear both devices getting the benefits of CGM and the benefits of an insulin pump separately. But they are not getting the benefit of an automated insulin delivery (AID) system where these two devices work directly together to adjust the amount of insulin delivered.
Automated Insulin Delivery Systems
With an automated insulin delivery (AID) system, the CGM sensor reads your glucose level and trend data and the system then determines the appropriate insulin dose to deliver. Mealtime or bolus insulin doses are still done by the user with the insulin pump, controller or smartphone app, depending on the system. Read more about AID systems here.
Omnipod 5 is an Automated Insulin Delivery (AID) System that works with leading CGM sensor brands. For compatible sensors with Omnipod 5 please see: Omnipod 5 Sensors. Omnipod 5 receives the glucose level and trend data from the CGM sensor and then automatically adjusts insulin every 5 minutes.
How do insulin pumps manage bolus or mealtime insulin doses?
As mentioned above, pumps deliver mealtime or bolus insulin doses via the insulin pump itself, a controller or smartphone depending on the system. Additionally, most have a bolus calculator feature to help with mealtime bolus suggestions, helping to simplify mealtime math.
One benefit of a pump is that you only need one type of insulin, commonly known as rapid-acting insulin. This is used for both your basal and bolus doses.
Understanding basal rates with Insulin Pumps
Basal rates are a crucial part of understanding pump therapy. These rates refer to the continuous delivery of small amounts of insulin throughout the day and night, mimicking the pancreas’s natural insulin release. This helps maintain stable blood glucose levels between meals and during sleep. Basal rates are sometimes referred to as “background” doses or background insulin.

Basal Rates and Insulin pumps without automation2
Insulin pumps that are not using automation are programmed to deliver personalized basal rates, measured in units per hour (U/hr), throughout the day and night depending on your needs.2 Real world data on insulin pump use in individuals with type 1 diabetes show benefits in A1c levels, and hypoglycemia reductions as well as total daily insulin reduction.3
Since most people with diabetes need different amounts of insulin at different times of the day, having multiple basal rates can be helpful.
The exact amount of insulin your body needs can change depending on
- Activity
- Stress
- Mealtimes
- Illness
- Schedule… and lots of other factors
If you’re currently on multiple daily injections, the idea of different basal rates sounds complicated. But not to worry, your healthcare provider will help determine the initial basal rates that fit your individual needs.
And at follow up visits, your healthcare provider can adjust your basal rates to address any changes in insulin needs.
With many insulin pumps (not using automation), basal insulin can be reduced or increased when needed by using a temporary basal rate. For example, you might use a temporary basal when exercising, or to help with the dawn phenomenon2 when your glucose levels naturally rise in the morning.
Basal Rates and Insulin pumps with automation
Automated Insulin Delivery (AID) Systems are insulin pumps that automatically adjust basal insulin every few minutes, based on real-time sensor values. These systems can reduce A1c levels and improve the amount of time spent in range.3
One example of this is Omnipod 5. The tubeless Pod is filled with rapid acting insulin and placed on the body. It then communicates with your CGM Sensor every 5 minutes to automatically increase, decrease or pause your insulin delivery according to your needs, day and night.5-7
Learn more about Automated Insulin Delivery.
Insulin Pumps: Bolus insulin doses
If your blood glucose is high or if you are planning to eat, you will need to take a bolus dose of insulin, sometimes referred to as a mealtime insulin dose.
These are not pre-programmed, and you must administer this yourself (or in the case of caregivers, on behalf of a child), with both AID systems and standard non automated insulin pumps.
However, insulin pumps have a bolus calculator built into the system which can suggest a dose based on your individual settings,2 as well as certain values like current glucose level and/or the carbohydrate value of your food.
Your healthcare provider will help you set up your individual settings, including what’s known as your ‘insulin to carb ratio’. If you do not use the calculator your healthcare provider may instruct you how much insulin to give at certain times.
Insulin pumps allow you to deliver insulin in very small doses - for example 0.025 or 0.05 unit increments! This precise dosing could help to improve blood glucose control.1
Insulin Pumps for Type 1 Diabetes
Managing type 1 diabetes means taking insulin to compensate for the insulin that the body no longer produces. While managing insulin doses daily can be challenging, insulin pump therapy offers convenience and the ability to customize insulin delivery to meet insulin needs.
The American Diabetes Association indicates that automated insulin delivery (AID) systems, are preferred over non automated insulin pumps and MDI for those with type 1 diabetes and have largely replaced the use of standard insulin pumps (non-automated).3
Learn more about this topic and explore how insulin pump therapy can simplify diabetes management for you or your loved ones here:
Insulin Pumps for Type 1 Diabetes
Insulin Pump Therapy for Children With Type 1 Diabetes
Insulin Pumps for Type 2 Diabetes
Many people with type 2 diabetes need to take insulin to manage their glucose levels, especially as the condition progresses. Initially, the pancreas may still produce some insulin, but over time, it often can’t produce enough or isn’t effective enough to meet glucose targets. Research shows that many people with type 2 diabetes who take insulin still struggle to achieve recommended glucose levels. Multiple daily injections (MDI) can be complex. Insulin pump therapy can simplify insulin management and reduce the physical and mental burdens of diabetes care.
The American Diabetes Association recommends automated insulin delivery (AID) systems as the preferred insulin delivery method (over non-automated insulin pumps and MDI) for children, adolescents and adults with type 2 diabetes.3
Explore our articles about Insulin Pump Therapy for Adults with Type 2 Diabetes and to learn the basics of insulin pump therapy and see if it might be the right choice for you or your loved one.
Other Frequently Asked Questions
Who would a pump be appropriate for?
Are insulin pumps painful?
Can I shower or swim with an insulin pump?
Do you sleep with an insulin pump?
Do I still need both types of insulin when using an insulin pump?
How much does an insulin pump cost?
Does Medicare pay for an insulin pump?
Can I get an insulin pump at my local pharmacy?
Why should I switch to a pump from MDI?
Continue reading:
Related Articles
Other topics
References and Disclaimers
*Fingersticks required for diabetes treatment decisions if symptoms or expectations do not match readings.
1. Berget C, Messer LH, Forlenza GP. A Clinical Overview of Insulin Pump Therapy for the Management of Diabetes: Past, Present, and Future of Intensive Therapy. Diabetes Spectr. 2019 Aug;32(3):194-204. doi: 10.2337/ds18-0091. PMID: 31462873; PMCID: PMC6695255.
2. Walsh, J, Roberts, R. Pumping Insulin. 6th ed. Torrey Pines Press. 2017.
3. American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee; 7. Diabetes Technology: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2026. Diabetes Care 1 January 2026; 49 (Supplement_1): S150–S165. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc26-S007
4. Majority defined as at least 50% of patient co-pays $30 or less per month. Among All Paid Omnipod 5 G7G6 Pods Commercial and Medicare Claims from January 2024 to December 2024. Includes benefits and offerings available through Insulet, such as the copay card program. Actual co-pay amount depends on patient’s health plan and coverage, they may fluctuate and be higher or lower than the advertised amount on a monthly basis. Source: IQVIA OPC Library
5. Brown S. et al. Diabetes Care (2021). Study in 240 people with T1D aged 6 - 70 years involving 2 weeks standard diabetes therapy followed by 3 months Omnipod 5 use in Automated Mode. Average time with high blood glucose in adults/adolescents and children, standard therapy vs 3-month Omnipod 5: 32.4% vs. 24.7%; 45.3% vs. 30.2%. Average time with low blood glucose in adults/adolescents and children, standard therapy vs 3-month Omnipod 5: 2.9% vs. 1.3%; 2.2% vs. 1.8%. Study funded by Insulet.
6. Sherr JL, et al. Diabetes Care (2022). Study in 80 people with T1D aged 2 - 5.9 yrs involving 2 weeks standard diabetes therapy followed by 3 months Omnipod 5 use in Automated Mode. Average time with high blood glucose in very young children, standard therapy vs 3-month Omnipod 5: 39.4% vs. 29.5%. Average time with low blood glucose in very young children, standard therapy vs 3-month Omnipod 5: 3.43% vs. 2.46%. Study funded by Insulet.
7. Pasquel FJ, et al. JAMA Network Open (2025). Prospective pivotal trial in 305 participants with T2D aged 18-75 yrs. Study included a 14-day standard therapy (ST) phase followed by a 13-week Omnipod 5 hybrid closed-loop phase. Mean time >180 mg/dL as measured by CGM: ST = 54%, 3-mo Omnipod 5 = 34%, P<0.001. Mean time <70 mg/dL as measured by CGM: ST = 0.2%, 3-mo Omnipod 5 = 0.2%.
These modules are not a replacement for medical advice or training. Please always speak to a qualified healthcare professional about your options.
The information and other content provided in this article, or in any linked materials, are not intended and should not be construed as medical advice, nor is the information a substitute for professional medical expertise or treatment. If you or any other person has a medical question or concern, you should consult with your healthcare provider. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something that have read on this blog or in any linked materials. If you think you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. The opinions and views expressed on this blog and website have no relation to those of any academic, hospital, health practice or other institution.
The Omnipod® 5 Automated Insulin Delivery System is indicated for use by individuals with type 1 diabetes mellitus in persons 2 years of age and older and type 2 diabetes mellitus in persons 18 years of age and older. The Omnipod 5 System is intended for single patient, home use and requires a prescription. The Omnipod 5 System is compatible with the following U-100 insulins: NovoLog®, Humalog®, Admelog®, and Kirsty®.
Available products subject to current insurance coverage and product indication for use. Insulet can only support onboarding for those customers within the product indication.
Refer to the Omnipod 5 Automated Insulin Delivery System User Guide and www.omnipod.com/safety for complete safety information including indications, contraindications, warnings, cautions, and instructions. Warning: DO NOT start to use the Omnipod 5 System or change settings without adequate training and guidance from a healthcare provider. Initiating and adjusting settings incorrectly can result in over-delivery or under-delivery of insulin, which could lead to hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia.